
- Red Hat Enterprise/CentOS: Git is included with Workstation and Server installation DVD. RPM package "git" although the version is often a little behind the current release: yum install git
For the current version of Git see RHEL 6 x86_64 or RHEL 7 x86_64 RPMs (yum install git2u-all) - Ubuntu/Debian: sudo apt-get install git
Installs packages: git-doc git-el git-arch git-cvs git-svn git-email git-daemon-run git-gui gitk gitweb
SSH and HTTP Git server configuration
A Git repository configured for a server will not require a working directory of checked-out code or a staging area as would a developer, thus it will only require a "bare" repository. Users will make git pull/push requests to the server to sync code. The server will be known as the "origin" repository.
The use of ssh to access the repository will require that each user have a system login.
For information on user accounts, see creating a new user system login.
Create Git repository:
- Set user identity:
- git config --global user.name "John Doe"
- git config --global user.email john.doe@megacorp.com
[user] name = John Doe email = john.doe@megacorp.com - Generate Repository:
- mkdir /srv/git/projectx
- cd /srv/git/projectx
- git init --bare --shared=group application1.git
- Use ssh-keygen to set up account keys
- git clone ssh://user@hostname:/srv/git/projectx/application1.git
Git client proxy configuration:
- git --global http.proxy http://proxy.megacorp.com:80
or - export HTTP_PROXY=proxy.megacorp.com:80
Configure repository:
- Make everything group readable and writable: git config core.sharedrepository 1
- Make sure that merges can't happen when you push to the repo. You have to do the merges on your local machine, and then push the result:
git config receive.denyNonFastforwards true
- Red Hat: Note that Red Hat does not have a package for Gitk. The latest version is available from github.com: gitk
wget https://raw.github.com/gitster/git/master/gitk-git/gitk
chmod +x gitk
This application requires Tcl/tk. - Mint/Ubuntu/Debian: apt-get install gitk
May also install dependency tk
Git-web is a Perl cgi web front-end to Git which allows one to view the Git repository.
Git-web Installation:
- Red Hat/CentOS: The RPM package gitweb-caching is available from the Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL) website and YUM repository
rpm -ivh gitweb-caching-1.6.5.2-8.b1ab8b5.el6.noarch.rpm
Installs to /var/www/gitweb-caching/... - Mint/Ubuntu/Debian: apt-get gitweb
CGI installs to /usr/lib/cgi-bin/gitweb.cgi
Configuration:
Configure git-web by creating the file /etc/gitweb.conf and place all changes to the configuration here. Do not edit the installation configuration.File: /etc/gitweb.conf
$projectroot = "/srv/git/projectx/git";
$site_name = "cm2.megacorp.com";
#$home_link_str = "http://cm2.megacorp.com/git-caching/"
$home_link_str = "GIT-Web";
# This just makes the description field wider so you can read # it better
$projects_list_description_width = 100;
# enable blame
$feature{'blame'}{'default'} = [1];
$feature{'patches'}{'default'} = [512];
Apache web server configuration file:
- Red Hat: /etc/httpd/conf.d/gitweb-caching.conf
- Mint/Ubuntu/Debian: /etc/apache2/conf.d/gitweb
Add the necessary authentication and authorization. See the YoLinux Apache authentication and authorization tutorial
[Potential Pitfall]: If you get the error in your Apache logs:
"... File does not exist: /var/www/gitweb-caching/gitweb.js, referer:. ..."
Download the file from the Git repo: git-1.7.6.1/gitweb/static/gitweb.js
File: /etc/gitweb.conf
$projectroot = "/srv/git"; ... ...
- The project root is just defined at a higher point in the directory tree. This will cover the repositories held in /srv/git/projectx/git and /srv/git/projecty/.git (for example).
- Use symbolic links to place all repositories under the same heirarchy if the repositories are scattered throughout the file system.

Trac Installation:
- Red Hat EPEL RPM downloads: https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/EPEL
Download the following RPM packages:- trac
Requires: python-genshi06 - trac-git-plugin
RPM package trac installs to:
/usr/bin/trac-admin /usr/sbin/tracd /var/www/cgi-bin/trac.cgi /var/www/cgi-bin/trac.fcgi /etc/trac/... /usr/lib/python2.6/site-packages/Trac-0.12.2-py2.6.egg-info/... /usr/lib/python2.6/site-packages/trac/... /usr/lib/python2.6/site-packages/tracopt/... /usr/share/doc/trac-0.12.2/...
- trac
- Mint/Ubuntu/Debian:
- apt-get install trac
This will also install the packages: libsvn1 python-genshi python-pygments python-setuptools python-subversion python-tz subversion - apt-get install trac-git
- apt-get install trac
- Location of Trac configuration: mkdir /srv/trac
- Initialize the Trac configuration: trac-admin /srv/trac/projectx initenv
Project Name [My Project]> projectx Database connection string [sqlite:db/trac.db]> - Give yourself admin privileges: trac-admin /srv/trac/midas/ permission add userx TRAC_ADMIN
- Allow the web server to own and access Trac: chown -R apache:apache /srv/trac
- SELinux:
- chcon -R -t httpd_sys_content_t /usr/share/trac/
- chcon -R -t httpd_sys_content_t /srv/trac/
Trac-git integration: also see the Trac GitPlugin wiki page
- mkdir /srv/trac
Trac configuration file: /srv/trac/projectx/conf/trac.ini
[trac] ... ## Best to use Trac with a "bare" and up to date repo. repository_dir = /srv/git/projectx/git/master ## repository_sync_per_request = (default) repository_type = git ... [git] cached_repository = true persistent_cache = true git_bin = /usr/bin/git split_page_names = false ## length revision sha-sums should be tried to be abbreviated to (must be >= 4 and <= 40); default: 7 shortrev_len = 40 ## (0.12.0.3+) minimum length for which hex-strings will be interpreted as commit ids in wiki context wiki_shortrev_len = 40 [header_logo] alt = Megacorp ProjectX height = -1 link = / src = /images/ProjectX_logo.png width = -1 [attachment] max_size = 8388608 render_unsafe_content = false # place at end of file [components] tracext.git.* = enabled
- Change default for logo and attachement max_size (I use 8388608)
- Use 40 char Git object IDs. The reason for this is because the Trac ticket reference to a commit must use all 40 characters in order to generate a proper hyperlink to the checked-in code.
Thus specify: shortrev_len = 40
Example:
[d64582ec9bf6e1bee0ee2e7084739be9c552614f]
or
rd64582ec9bf6e1bee0ee2e7084739be9c552614f (prefixed with "r")This "wiki format" will generate hyperlinks to the Git commit info. Partial Git object IDs will not work.
This capability is only available in Trac 0.12 and later.
Trac configuration file: /srv/trac/projectx/conf/trac.ini[trac] repository_sync_per_request = ... [repositories] projectx.description=Project X projectx.dir = /srv/git/projectx/git/master projectx.type = git projectx.url = ssh://localhost/srv/git/projectx/git/master projecty.description=Project Y projecty.dir = /srv/git/projecty/.git projecty.type = git projecty.url = ssh://localhost/srv/git/projecty/.git [git] cached_repository = false ...
- Use 40 char Git object IDs and the repository identifier assigned when referencing the Git check-in hash code. The repository identifier is required to distinguish which repository to use.
Example:
[d64582ec9bf6e1bee0ee2e7084739be9c552614f/projectx]
or
[changeset:d64582ec9bf6e1bee0ee2e7084739be9c552614f/projectx]This "wiki format" will generate hyperlinks to the Git commit info. Partial Git object IDs will not work. The "r" prefix also does not seem to work as it does with a single repository.
- Set cached_repository = false for a repository with more than 500 commits. Caching seems to bog things down as a repo grows.
- A default code tree can be displayed by adding:
.alias = projectxThis will display the projectx code tree when you go to the source browser. The default without this line is to show only the top starting link. This may be omitted to keep the page simple if the page is too cluttered. - The single repository references in the [trac] section are removed:
- Remove repository_dir = /srv/git/projecx/git/master
- Remove repository_type = git
Git post-commit hooks to update Trac:
File: /srv/git/projectx/git/master/hooks/post-commit
#!/bin/sh REV=$(git rev-parse HEAD) trac-admin /srv/trac/projectxy changeset added projectx $REV
File: /srv/git/projecty/.git/hooks/post-commit
#!/bin/sh REV=$(git rev-parse HEAD) trac-admin /srv/trac/projectxy changeset added projecty $REV
- there is a single Trac instance /srv/trac/projectxy but two Git repositories: projectx and projecty.
- These are executable scripts to be executed by Git.
Trac Admin page for defining multiple repositories:
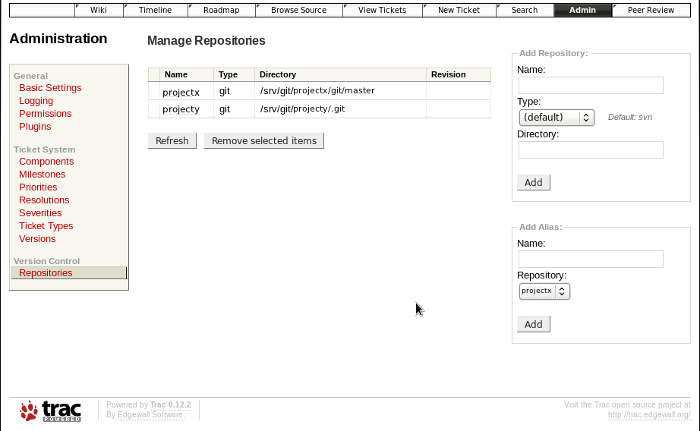
Trac can be run using the stand-alone Trac daemon "tracd". This configuration shows the use of Apache with Trac.
File: /etc/httpd/conf.d/trac.conf
(Red Hat location)
- This example performs no authentication:
Note: The path /var/www/cgi-bin/ is Red Hat specific.
Alias /trac/ /var/www/cgi-bin/trac.cgi <LocationMatch /cgi-bin/trac\.f?cgi"> SetEnv TRAC_ENV_PARENT_DIR "/srv/trac" </LocationMatch> <IfModule mod_python.c> <Location /trac> SetHandler mod_python PythonInterpreter main_interpreter PythonHandler trac.web.modpython_frontend PythonOption TracEnvParentDir /srv/trac </Location> </IfModule>Restart Apache: service httpd restart
The final touch is to create a homepage for your repositories so that they are easy to find, especially if you are hosting multiple reporitories. The default homepage for most major Linux distributions (Red Hat, Fedora, CentOS, Ubuntu, Debian) is /var/www/html/index.html Create a home page here or create a redirect to the Trac Wiki home page and post links there.
Redirect to the Trac Wiki<META HTTP-EQUIV="Refresh" Content="0; URL=/trac/projectx">Sample home page:
<html> <head> <title>Welcome to Project X</title> </head> <body> <h1>Welcome to Project X</h1> <ul> <li> <a href="/trac/projectx">Trac Wiki</a> </li> <li> <a href="/git-caching/">Git-web</a> </li> <li> <a href="/jenkins">Jenkins</a> </li> </ul> </body> </html>
- Git home page
- Trac home page
- Git Plugin for Trac - Trac-Hacks
- YoLinux.com Subversion and Trac tutorial - lots of Trac administration information. Hosting multiple Trac projects, etc.
- YoLinux.com Jenkins tutorial - will require the use of the Jenkins "git" plugin.

 Books:
Books:






