| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| CD-R | CD-Recordable. Write Once, Read Many. (WORM) |
| CD-RW | CD-Rewritable. Write Many, Read Many. |
| ISO-9660 | DOS compatible file system (8.3 character file names) for CD's. Requires extensions like "Rock Ridge" to fully support UNIX/Linux |
| Rock Ridge | ISO-9660 extension to allow long file names, UNIX symlinks and file protection (rwx). Windows readable. |
| Joliet | Microsoft extension to ISO-9660. Creates MS/Windows 95 like 8.3 file names with translation to 64 character names. |
| Multisession | Allows adding/writing files at a later time. Session must be closed before it is readable. |
| DAO | Burn entire audio CD at once in a single burn. It's the only way to avoid delays between tracks |
| TAO | Burn a track at a time. Results in 2 second delay between audio tracks. |
- X-CdRoast
- GNOME Nautilus
- GNOME Brasero: - designed to be simple
- GNOME Toaster
- Disc-O-Matic - CD/DVD archiving tool
- ECLipt Roaster - GTK interface to mkisofs and cdrecord for writing CDs on the fly.
- K3b - KDE CD burning front end
- SSCDRFE - Qt based Small Simple CDR front end
- TkBurn
Within the Nautilus file manager is "CD Creator".
Note: Some systems require that you be root. Also see the YoLinux.com Managing groups tutorial to configure a system to grant users CD privileges.
File or directory backup:
- Launch "CD Creator" using one of the following methods:
- Insert blank CD-R(W), Nautilus "CD Creator" will appear
- Type the URL "burn:///" in Nautilus.
- From the Nautilus toolbar select "Go" + "CD Creator".
- Select the "Home Folder" within the tree portion of the GUI
OR: launch a new instance of the Nautilus file manager by double clicking the "Home" icon on the desktop.
Select files and directories to back-up. Use ctrl key for multiple selections.
Right click to bring up an options menu and select "Copy File". (or Cut, ...)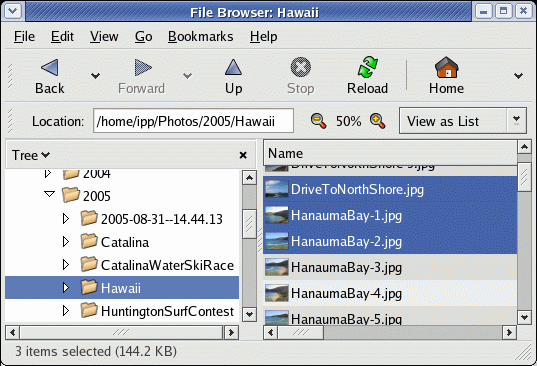
- Select the "Blank CD-R Disk:" item in the "Tree"
OR: If using two Nautilus windows, drag files/directories to the "CD Creator" window.
Right click to bring up an options menu and select "Paste Files".
[Potential Pitfall]: When the blank CD is inserted into the drive, Nautilus should start with a CD showing no contents. If the contents from the last burn remail listed, select them and press the "delete" key to remove the listing. - Select the "Write to Disc" button.
- This will launch a new dialog box "Write to Disc".
Select the "Write" button: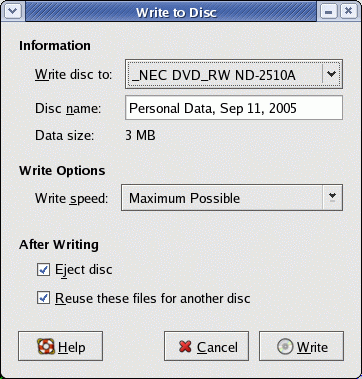
- This will burn a CD with the contents you dropped in the "Blank CD-R Disc" branch of the Tree menu.
CD/DVD system behavior configuration for the Gnome desktop:
Set system behavior using the Gnome command gnome-volume-properties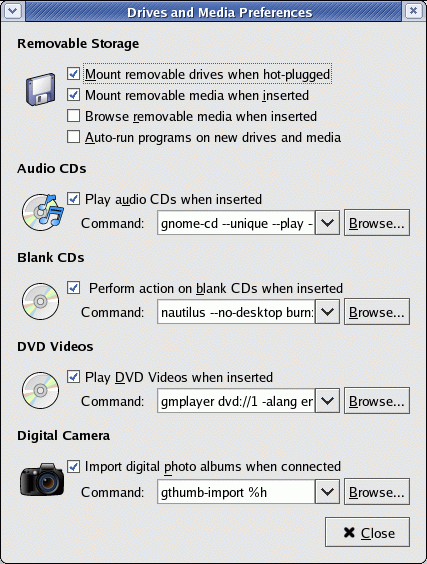
- cdrecord: Home Page - man page - [Downloads] - Command line interface to burn CD's TAO and DAO.
- mkisofs: man page - Build an ISO file system image. (as a file on hard drive)
- mkisofs-md5: mkisofs-md5 - an advanced edtion for original mkisofs
- cdparanoia: Home Page - cdparanoia man page - audio CD reading utility
- cdrdao: Home Page - cdrdao man page - Burn audio CDs without introducing 2 second gaps between tracks. Best for duplicating audio CDs. (Burns DAO-Disk At Once instead of TAO-Track At Once) Supports drives working in raw mode only. List of supported drives. Also has Xcdrdaow front-end.
Downloads:
- cdrecord, mkisofs and cdda2wav RPM's available from this page
- cdrdao RPM packages are available or download source:
[download cdrdao]
This in turn requires gtk-- which is also available as an RPM on the Red Hat Powertools CD.
Note: Use the command cdrecord -scanbus to scan your SCSI bus to determine the device description. (i.e. 0,4,0). This will perform a scan and provide results for real SCSI systems or for the virtual SCSI subsystem Linux uses with IDE CD/DVD's.
Examples:
- SCSI CD system:
# cdrecord -scanbus Cdrecord 1.8 (i686-pc-linux-gnu) Copyright (C) 1995-2000 Jorg Schilling Using libscg version 'schily-0.1' scsibus0: 0,0,0 0) 'SEAGATE ' 'ST36530W ' '1498' Disk 0,1,0 1) 'SEAGATE ' 'ST39173W ' '6244' Disk 0,2,0 2) * 0,3,0 3) * 0,4,0 4) 'HP ' 'CD-Writer+ 9200 ' '1.0c' Removable CD-ROM 0,5,0 5) * 0,6,0 6) * 0,7,0 7) * - CD/DVD ATA system: This will report on your SCSI device name to use when burning a CD. In this case "ATA".
# cdrecord -scanbus Cdrecord-Clone 2.01-dvd (--) Copyright (C) 1995-2004 Jorg Schilling ... scsidev: 'ATA' devname: 'ATA' scsibus: -2 target: -2 lun: -2 Linux sg driver version: 3.5.27 Using libscg version 'schily-0.8'. cdrecord: Warning: using unofficial libscg version (schily Red Hat-scsi-linux-sg.c-1.83-RH scsibus1: 1,0,0 100) '_NEC ' 'DVD_RW ND-2510A ' '2.15' Removable CD-ROM 1,1,0 101) * 1,2,0 102) * 1,3,0 103) * 1,4,0 104) * 1,5,0 105) * 1,6,0 106) * 1,7,0 107) *
[Potential Pitfall]: You may have to be root to access the CD with the appropriate permissions.
Cdrecord 1.10 (i686-pc-linux-gnu) Copyright (C) 1995-2001 Jorg Schilling
cdrecord: Permission denied. Cannot open '/dev/sg0'. Cannot open SCSI driver.
cdrecord: For possible targets try 'cdrecord -scanbus'. Make sure you are root.
Note:
- Linux Kernel 2.2 and 2.4 use SCSI emulation when accessing an IDE/ATAPI
CD drive. See "IDE and Linux Kernel considerations" below.
Example device reference: dev=0,4,0 - Linux kernel 2.6 allows one to directly access ATAPI. Prefix the
device name with "ATAPI:".
Example device reference: dev=ATAPI:0,4,0 - To get a list of supported devices: cdrecord dev=HELP
i.e.: ATAPI, ATA, RSCSI (remote scsi)
Note:
- Data CD's must be mounted before one may access them. The CD may be mounted
by:
- The automounter
OR - The graphical mounting tool "Start" + "System" + "Disk Management" + "Mount"
OR
/usr/bin/usermount
OR - The mount command:
- Red Hat 7/8/9: mount -r -t iso9660 /dev/cdrom /mnt/cdrom
- Fedora Core 3 (kernel 2.6): mount -r -t iso9660 /dev/hdc /media/cdrecorder
Note: Fedora Core 3 is using /media as a mount point for floppy drives, CD-ROMs and DVDs.
This command should work for a Red Hat installation. Other distributions may require the set-up as described in the YoLinux Sys Admin Tutorial - Mounting a CD.
Don't forget to un-mount the CD with umount /mnt/cdrom
[Potential Pitfall]: There is NO "N" in umount!!! - The automounter
- It is often required that the user be root in order to perform
these functions. Switch user using the command "su -" then enter the
appropriate password.
Run the CD burning commands as root as this is typically the only user on the system with privileges to burn a CD. One may also configure user groups and permissions to grant access for a user to burn a CD. See the YoLinux tutorial Managing Group Access.
Use the command "cdrecord" as described above to obtain entries for the "dev" and "--device" command line arguments.
Data CD's will require that you create the ISO image first (use command mkisofs) and then burn the ISO image onto the CD (use command cdrecord). See mkisofs instructions below.
Examples:
- If you download an ISO CD image from the internet (i.e. a Linux CD) for your favorite Linux distro or possess a CD you wish to copy:
- Create ISO image file:
- Copy a data CD (fast):
cat /dev/scd0 > RedHat-7.0-i386-powertools.iso
or - Mount CD to copy: mount -t iso9660 -o ro /dev/cdrom /mnt/cdrom
(Fedora core 3 (kernel 2.6): mount -t iso9660 -o ro /dev/cdrom /media/cdrecorder)
Create ISO file image copy of CD: mkisofs -r -o RedHat-7.0-i386-powertools.iso /mnt/cdrom
- Copy a data CD (fast):
cat /dev/scd0 > RedHat-7.0-i386-powertools.iso
- Burn ISO image onto CD:
- Linux 2.6 kernel: cdrecord -v -eject speed=16 dev=ATA:1,0,0 RedHat-7.0-i386-powertools.iso
- Linux 2.4 kernel: cdrecord -v speed=2 dev=0,4,0 RedHat-7.0-i386-powertools.iso
(Tip: Mounting the raw ISO file: mount -t iso9660 -o loop /home/user1/RedHat-9.0-i386-Disk1.iso /mnt/iso-1)
- Create ISO image file:
- Backup a directory to a CD:
- One step: mkisofs -r -R -J -l -L /home/user1 | cdrecord dev=0,4,0 -v --eject speed=4 -
- or the two step variation of the process:
- mkisofs -r -R -J -l -L -allow-multidot -o /tmp/backup.iso -graft-points "/home/user1=/home/user1"
- cdrecord dev=0,4,0 -v --eject speed=4 /tmp/backup.iso
Make sure directory does not hold more than CD capacity (700Mb typically). Check with the command: du -s /home/user1 - Copy a data CD:
Mount CD to copy (kernel 2.4): mount -t iso9660 -o ro /dev/cdrom /mnt/cdrom
(Linux kernel 2.6: mount -t iso9660 -o ro /dev/cdrom /media/cdrecorder)
Create ISO file image copy of CD: mkisofs -r -R -J -l -L -o /tmp/cd-iso-image-file.iso /mnt/cdrom
Unmount: umount /mnt/cdrom (or umount /media/cdrecorder)
Load blank CD to burn.
Burn CD examples:- Linux kernel 2.4: cdrecord -v speed=2 dev=0,4,0 -data /tmp/cd-iso-image-file.iso
(SCSI bus 0, device 4, lun 0) - Linux kernel 2.6: cdrecord -v speed=2 dev=ATA:1,0,0 /tmp/cd-iso-image-file.iso
Note: The flag -data is default unless audio file extensions .au or .wav are used which defaults to -audio.
- Linux kernel 2.4: cdrecord -v speed=2 dev=0,4,0 -data /tmp/cd-iso-image-file.iso
- Burn a multisession CD:
This is easiest with X-CdRoast which can perform the necessary calculations but it can also be done via the command line.
cdrecord -v -eject speed=4 dev=0,4,0 -multi cd-iso-image-file-1.iso
The CD is left in a mode which will allow it to receive more data.
To append data one must know where the last burn left off:
cdrecord dev=0,4,0 -msinfo
This will give you the starting and ending track numbers. i.e.: 0,16774. Use this result in mkisofs.
mkisofs -J -r -V SecondBurn -o cd-iso-image-file-2.iso -C 0,16774 -M 0,4,0 directory-with-files-to-add
The TOC from the first and second session will be combined.
Note: Omit the option "-multi on the final burn. - Copy then burn single audio tracks TAO:
cdda2wav -D 0,4,0 -B /tmp/prefix-of-music-files
The files will be written out as /tmp/prefix-of-music-files_01.inf /tmp/prefix-of-music-files_01.wav /tmp/prefix-of-music-files_02.inf ...- Linux 2.6 kernel: cdrecord -v speed=2 dev=ATA:1,0,0 -audio /tmp/prefix-of-music-files*.wav
- Linux 2.4 kernel: cdrecord -v speed=2 dev=0,4,0 -audio /tmp/prefix-of-music-files*.wav
- Burn audio tracks DAO:
Copy to hard drive:
cdda2wav -D 0,4,0 -g -O wav -S 1 -v30 -P 0 -n 75 -B /tmp/CD/track-01.wav /tmp/CD/track-02.wav ...
Burn CD:- Linux 2.6 kernel: cdrecord dev=ATA:1,0,0 fs=4096k -v -useinfo speed=1 -dao -eject -pad -audio "/tmp/CD/track-01.wav" ...
- Linux 2.4 kernel: cdrecord dev=0,4,0 fs=4096k -v -useinfo speed=1 -dao -eject -pad -audio "/tmp/CD/track-01.wav" ...
- Burn WAV files:
- Linux 2.6 kernel: cdrecord dev=ATA:1,0,0 -eject speed=16 -pad -audio *.wav
- Linux 2.4 kernel: cdrecord dev=0,4,0 -eject speed=2 -pad -audio *.wav
- Copy then burn audio CD's DAO (two drives): See cdrdao examples
Copy the CD from the reader (SCSI 3) and burn on the Read/Writer (SCSI 4):
cdrdao copy --source-device 0,3,0 --device 0,4,0 --buffers 64
OR
cdrdao copy --source-device 0,3,0 --source-driver generic-mmc-raw --device 0,4,0 --driver generic-mmc-raw --buffers 64 toc-file.toc - Copy audio CD DAO with one CD drive:
cdrdao copy --device 0,4,0 --buffers 64 --driver generic-mmc-raw --read-raw toc-file.toc
This will prompt you to insert the CD-R after an image of the source CD was created. ("Please insert a recordable medium and hit enter") The image file with name "cddata<pid>.bin" will be created in the current working directory. (file removed when done) - Extract audio image from CD:
cdrdao read-cd --device 0,4,0 --buffers 64 --driver generic-mmc-raw --read-raw toc-file.toc
Creates file data.bin and table of contents file toc-file.toc. This is NOT a fast process. - Finalize a disk:
- CD: cdrecord -fix -dev=/dev/cdrw
- DVD: cdrecord -fix -dev=/dev/dvdrw
[Potential Pitfall]: You may get the following error if mounted:
$ sudo cdrecord -fix -dev=/dev/cdrw [sudo] password for user1: Error trying to open /dev/cdrw exclusively (Device or resource busy)... retrying in 1 second. Error trying to open /dev/cdrw exclusively (Device or resource busy)... retrying in 1 second. Error trying to open /dev/cdrw exclusively (Device or resource busy)... retrying in 1 second.Unmount the device first: sudo umount /media/CDROM
- Audio CD's do not have a file system thus they cannot be mounted, just read.
Audio CD's can represent frequencies up to 22.05 kHz and at a sample rate of 44.1 kHz.
- ISO 9660 refers to a data CD storage format and not to the standard audio CD.
- Don't run any applications while burning as this can lead to buffer
under-run condition if your PC was not able to allocate enough time to
processing the burn. This will then create a useless CD.
- I use a SCSI CD but for those that are using IDE you may be required to
add the following entry to the end of /etc/lilo.conf and execute lilo -v. This allows linux to use a SCSI interface to the IDE CD drive.
append = "hdb=ide-scsi" (loads kernel loadable module: /lib/modules/2.X.XX-XX/kernel/drivers/scsi/ide-scsi.o)
OR
at the lilo boot prompt enter linux hdb=ide-scsi - Want to hear that wav file to make sure it is the right song?
play file_01.wav - Assign a higher priority to the process burning the CD: nice -18 cdrecord ...
Where the priority range is 19 (lowest) to -20 (highest). Default is 10. - Device defaults can be found in the configuration file: /etc/cdrecord.conf
The default speed can be set: CDR_SPEED=4
The re-writable CD can be "blanked" before re-burning. (optional)
- Using XCdRoast GUI:
- "Create CD"
- "Write Tracks"
- "Blank CD-RW"
- Command to "blank" a CD-RW:
- Fast blanking. Data is not overwritten:
cdrecord dev="1,0,0" -v -eject speed=4 blank=fast
- Full blanking. Data is overwritten and entire media is erased:
cdrecord dev="1,0,0" -v -eject speed=4 blank=all
- Fast blanking. Data is not overwritten:
An ISO 9660 standard CD is a mountable file system. One may first generate an ISO image of the data files and directories on the hard drive before burning the CD. Once this is generated, it can be burned directly onto the CD. This is the standard used for data CD's and NOT the standard used for your typical CD player. The mkisofs command is used to generate an ISO image. The command cdrecord can then be used to burn an ISO image onto the CD.
Examples:
- Copy a directory tree from the hard drive into an ISO-9660 image:
(for the preferred Linux backup see the next option.)
mkisofs -r -o /fully-qualified-file-name-of-iso-image.iso /name-of-directory-containing-files-to-format-into-iso-image - Copy an existing CDROM into a new ISO-9660 image:
mkisofs -r -o /fully-qualified-file-name-of-iso-image.iso /dev/cdrom - Copy a directory tree from the hard drive into an ISO image (but probably not
compatible with MS DOS):
(Better for Linux backup as hidden files beginning with "." and
long file names are preserved.)
mkisofs -r -R -J -l -L -o /fully-qualified-file-name-of-iso-image.iso /name-of-directory-containing-files-to-format-into-iso-image - Example of command used to make Red Hat Power Tools CD:
mkisofs -A Red Hat Powertools/i386 7.1 -V Red Hat Powertools/i386 7.1 -r -R -J -v -T -x ./lost+found -o /ISO/Powertools-7.1-i386.iso - Example of command to create Red Hat boot/install disk:
mkisofs -A Red Hat Linux/i386 7.1 -V Red Hat Linux/i386 7.1 -J -r -R -v -T -x ./lost+found -o /ISO/qa0408.4-i386-disc1.iso -b dosutils/autoboot/cdboot.img -c boot.cat - Write Multiple directories to CD and place in a root directory of the assigned name: (Command is all on one line.)
mkisofs -r -R -J -l -L -o /ISO/MyBackupCD-20031214.iso -graft-points "/=/home/user1/DirectoryNameA" "/=/home/user1/DirectoryNameB/SubDirectoryNameC" "/=/home/user1/DirectoryNameD/FileName_1" "/=LocalDirectoryNameE"This will create a CD ISO image with the following directory structure:
/FilesFromDirectoryNameA_1 /FilesFromDirectoryNameA_2 ... /SubDirectoryFromDirectoryNameA/... /FilesAndDirectoriesFromDirectoryNameC/... /FileName_1 /FileFromLocalDirectoryNameE_1 /FileFromLocalDirectoryNameE_2 /FileFromLocalDirectoryNameE_3 /...Note:- The last directory specified in the path name is NOT put on the CD but it's contents are.
- The reference to LocalDirectoryNameE is the directory which can be listed from the directory where the mkisofs command is issued.
- Double check what you created by mounting the ISO image (see below) and viewing the files.
- Specify root directory name of copied directories: (Command is all on one line.)
mkisofs -r -R -J -l -L -o /ISO/MyBackupCD-20031214.iso -graft-points "/DirectoryNameA=/home/user1/DirectoryNameA" "/SubDirectoryNameC=/home/user1/DirectoryNameB/SubDirectoryNameC"This will create a CD ISO image with the following directory structure:
/DirectoryNameA/...
Note:
/SubDirectoryNameC/...
- When referencing a local directory sometimes one must end
the CD directory name with a closing "/" in order to have the directory
created on the CD. This was true with older versions (RH 8.0 but not
9.0) of mkisoffs:
-graft-points "/CD-dirname/=HardDriveLocal-dirname"
- When referencing a local directory sometimes one must end
the CD directory name with a closing "/" in order to have the directory
created on the CD. This was true with older versions (RH 8.0 but not
9.0) of mkisoffs:
- The last directory specified in the path name is NOT put on the CD but it's contents are.
mkisofs options:
| Command Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -b | Specifies the path and filename of the boot image to be used when making an "El Torito" bootable CD.
The pathname must be relative to the source path specified to mkisofs. Required to make a bootable CD. The boot image must be exactly the size of either a 1.2, 1.44, or a 2.88 meg floppy. |
| -c | Specifies the path and filename of the boot catalog to be used when making a bootable CD.
The pathname must be relative to the source path specified to mkisofs. |
| -l | Allow 31 character file names. CD will not be 8.3 DOS compatible. (Who cares! Thus use this option.) |
| -o | Name of iso9660 output image file |
| -r | Set file permissions on CD to be publicly readable |
| -v | Verbose execution. |
| -x | Exclude given path from being written to CDROM. |
| -A | Text string that will be written into the volume header |
| -J | Generate Joliet directory records in addition to regular iso9660 file names. This preserves the case (upper/lower) of file and directory names. Useful for use with MS/Windows environments. |
| -L -allow-leading-dots |
Allows files to begin with "." (period). Use this option to write Unix/Linux hidden files. CD will not be DOS compatible. (Who cares! Thus use this option.) |
| -allow-multidot | Allows files to contain multiple "."s (periods). Use this option to write Unix/Linux files which may contain more than one period. CD will not be DOS compatible. (Who cares! Thus use this option.) |
| -R | Add Rock Ridge records to further describe the files. Preserves filename length and case. |
| -V | Specifies the volume ID to be written into the master block. |
| -T | Generate a file TRANS.TBL in each directory. |
| -graft-points | Translate a directory to the root ("/") of the CD. See examples. (i.e.: -graft-points "/=DirectoryName/") |
| -pad | Default (not necessary to specify this option). Pads the end of the whole image by 150 sectors (300 kB). Avoids read ahead errors on last file. |
More info:
Ripping an entire CD/DVD to an ISO image:
- Copy all the data from a CD/DVD: cat /dev/scd0 > data.iso
Note: This will not pick up the MBR from a bootable installation CD or DVD. - Copy all the data from a CD/DVD:
- DVD dev link: dd if=/dev/dvd of=/tmp/isofile.iso
- SATA/EIDE: dd if=/dev/hdc of=/tmp/isofile.iso
(View device name: "dmesg|grep DVDR" or "df") - SCSI: dd if=/dev/scd0 of=/tmp/isofile.iso
Note: This will capture boot information from a bootable CD or DVD.
Also good for ripping a video DVD to an ISO image for duplication. - Create ISO file image copy of CD: mkisofs -r -R -J -l -L -o /tmp/cd-iso-image-file.iso /mnt/cdrom
Note: The CD must be mounted first.
Ripping an audio CD:
See examples of ripping audio CDs (above) in this tutorial or the YoLinux.com MP3 tutorial: Ripping MP3s.
Ripping video from a video DVD:
Check the title (play title 4): mplayer dvd://4
(It will also tell you the number of titles, chapters and other stats like frame rate (fps), bit rate (kbps), etc.)
Rip DVD video:
- Re-encode DVD video to specified AVI: mencoder dvd://4 -ovc lavc -oac copy -o title4.avi
- Do not re-encode DVD video (just dump): mplayer -dumpstream dvd://4 -dumpfile title4.mpeg
(DVD original quality video. The penalty is the much larger file size.)
This is the same as cp /media/cdrecorder/VIDEO_TS/VTS_01_1.VOB title1.mpeg
The DVD "VOB" file typically is an MPEG (I or II) video although all variations are not allowed.
Full video and sound are captured. The DVD video format allows for multiple language sound tracks thus copying a movie released in multiple languages may have surprising audio results.
After you have created an ISO 9660 image file, one can verify it's contents by mounting the raw ISO file as a file system.
mount -t iso9660 -o loop /home/user1/RedHat-9.0-i386-Disk1.iso /mnt/iso-1This can also be mounted using an entry in the file: /etc/fstab
/home/user1/RedHat-9.0-i386-Disk1.iso /mnt/iso-1 iso9660 loop,ro 0 3
Sharing the ISO by http:
The mounted IS can be shared via Apache httpd with the following configuration file: /etc/httpd/conf.d/iso-share.conf
Alias /iso /mnt/iso-1
<Directory /iso /mnt/iso-1>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
Order deny,allow
Allow from all
</Directory>
The isoinfo utility can be used to gather information in a ISO file or on a CD and verify the integrity of an iso9660 image.
| Command Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -h | Help and summary of options |
| -d | Primary volume descriptor (PVD) of iso9660 image. |
| -f | Use find output formatting |
| -i /path-of-image or dev=/dev/cdrom |
Path of image to examine or specify device (one or the other, not both) |
| -p | Output path table information |
| -R | Print permissions, file names and ownerships (Rock Ridge extensions) |
| -J | Print file names (Joliet extensions) |
| -T sector | Print info about multi-session images. |
Examples:
- List contents of an iso file: isoinfo -f -R -i isoFile.iso
- List info about a CD: isoinfo -d -i /dev/cdrom
CD-ROM is in ISO 9660 format System id: LINUX Volume id: FC/3 x86_64 Volume set id: Publisher id: Data preparer id: Application id: FC/3 x86_64 Copyright File id: Abstract File id: Bibliographic File id: Volume set size is: 1 Volume set sequence number is: 1 Logical block size is: 2048 Volume size is: 326239 El Torito VD version 1 found, boot catalog is in sector 123 Joliet with UCS level 3 found Rock Ridge signatures version 1 found Eltorito validation header: Hid 1 Arch 0 (x86) ID '' Key 55 AA Eltorito defaultboot header: Bootid 88 (bootable) Boot media 0 (No Emulation Boot) Load segment 0 Sys type 0 Nsect 4 Bootoff 7C 124Note: The block and volume size can be used as input to the following command to:- Find the check sum of the CD:
dd if=/dev/cdrom bs=2048 count=326239 conv=notrunc,noerror | md5sum
(Linux 2.6 kernel 2.6: /media/cdrecorder) - Create an iso image:
dd if=/dev/cdrom bs=2048 count=326239 conv=notrunc,noerror > file-name.iso
- Find the check sum of the CD:
Man Pages:
The "Disc at once" (DAO) feature allows one to burn an audio CD without the two second gap between tracks. This is most useful when copying CDs as it allows one to burn the CD to be just like the original. The cdrdao command uses a "table of contents" (TOC) file as shown below.
Usage: cdrdao command [options] toc-file
Example: cdrdao write toc-file.toc
| command | Description |
|---|---|
| show-toc | Prints out table of contents (toc) then exits |
| toc-info | Prints out short toc-file summary |
| toc-size | Prints total number of blocks for toc |
| read-toc | Create toc file from audio CD |
| read-cd | Create toc and rip audio data from CD |
| show-data | Prints out audio data and exits |
| read-test | Reads all audio files and exits |
| disk-info | Shows information about inserted medium |
| unlock | Unlock drive after failed writing |
| simulate | Shortcut for 'write --simulate' |
| write | Writes CD |
| copy | Copies CD |
| option | Description |
|---|---|
| --device x,y,z SCSI bus, device, lun i.e. 0,4,0 |
Sets SCSI device of CD-writer |
| --source-device x,y,z | sets SCSI device of CD-ROM reader (used by 'copy') |
| --driver driver-id | Force usage of specified driver |
| --source-driver driver-id | Force usage of specified driver for source device (used by 'copy') |
| --simulate | Perform a write simulation |
| --speed CD-speed | Set writing speed |
| --multi | Session will not be not closed |
| --eject | Ejects cd after writing or simulation |
| --swap | Swap byte order of audio files |
| --on-the-fly | No image file is created. Perform copy in process. |
| --datafile file-name | Name of toc file Used by read-toc, read-cd and copy |
| --buffers number | Sets fifo buffer size (min. 10, def 32) |
| --session number | Selects session for read-toc/read-cd |
| --fast-toc | Do not extract pre-gaps and index marks |
| --read-raw | Read raw sectors for read-cd |
| --paranoia-mode number | DAE paranoia mode (0..3) |
| --reload | Reload the disk if necessary for writing |
| --force | Force execution of operation |
| -v verbose-level | Set verbose level |
| -n | No pause before writing |
See cdrdao examples and how to generate a toc file to control gaps (or lack thereof) during CD burn.
Create toc (table of contents file) which shows(read)/determines(write)
the gaps in tracks.
cdrdao read-toc --driver generic-mmc-raw --read-raw --device 0,4,0 toc-file.toc
Sample TOC (Table Of Contents) file:
CD_DA
CATALOG "0075590506829"
// Track 1
TRACK AUDIO
NO COPY
NO PRE_EMPHASIS
TWO_CHANNEL_AUDIO
SILENCE 00:01:00
FILE "data.wav" 0 03:28:70
START 00:01:00
// Track 2
TRACK AUDIO
NO COPY
NO PRE_EMPHASIS
TWO_CHANNEL_AUDIO
FILE "data.wav" 03:28:70 02:14:45
START 00:04:52
...
..
// Track 10
TRACK AUDIO
NO COPY
NO PRE_EMPHASIS
TWO_CHANNEL_AUDIO
FILE "data.wav" 26:05:40 05:03:37
// Track 11
TRACK AUDIO
NO COPY
NO PRE_EMPHASIS
TWO_CHANNEL_AUDIO
FILE "data.wav" 31:09:02 04:50:50
Minimal example:
CD_DA TRACK AUDIO AUDIOFILE "song1.wav" 0 TRACK AUDIO AUDIOFILE "song2.wav" 0 TRACK AUDIO AUDIOFILE "song3.wav" 0 ... ..Where the "0" refers to the beginning of the file
Links:
- Sourceforge: cdrdao Home Page
- GcdMaster - GNOME CDRDAO GUI for CD mastering
Most kernels as released by the various Linux distributions include SCSI emulation support and thus support for the IDE CD drive. Check this with the following command: dmesg | grep -i scsi
SCSI subsystem initializedThis shows that the SCSI subsystem is working. (example: Fedora Core 3)
scsi0 : sata_via
scsi1 : sata_via
The Linux kernel 2.6 (RH Fedora Core) can use ATAPI directly by prefixing "ATAPI:" (or for ATA devices, ATA:) to the device argument.
If using Linux kernel 2.2 or 2.4, SCSI emulation is required.
The kernel module ide-scsi enables this support.
The Linux CD interface uses SCSI as a hardware interface with Linux kernel 2.2 or 2.4. If you have an IDE/ATAPI CD and Linux kernel 2.2 or 2.4, you must use Linux SCSI emulation. Compile this in as part of your kernel by adding the following support using "make xconfig":
- Block devices -> Include IDE/ATAPI CDROM support = n
- Block devices -> SCSI emulation support = y
Support for SCSI controller card support should be disabled.
Linux kernel configuration parameters:
| Kernel config parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| CONFIG_ISO9660_FS=y | ISO CD-ROM file system support. |
| CONFIG_BLK_DEV_IDE=y CONFIG_BLK_DEV_IDECD=y |
IDE/ATAPI CD-ROM device support. |
| CONFIG_SCSI=y CONFIG_CHR_DEV_SG=y CONFIG_SCSI_device-specific-driver=y |
SCSI CD-ROM device support. (generic and driver specific) |
| CONFIG_UDF_FS=y | DVD file system support. |
| CONFIG_UDF_RW=y | Read/Write DVD file system. |
See YoLinux Optimization: Compiling the Kernel
The SCSI driver is loaded when the kernel boots and is held in:
- Fedora Core 3: /etc/modprobe.conf
- Red Hat 7/8/9: /etc/modules.conf
- Red Hat (or for older systems) 5: /etc/conf.modules
- Debian /etc/modules
alias scsi_hostadapter aic7xxxExamples for IDE systems:
alias scsi_hostadapter sata_via
or
alias scsi_hostadapter ide-scsi
The module can be loaded manually: insmod ide-scsi
and
removed manually: rmmod ide-scsi
On systems with an IDE/ATAPI CD-Rom, the system will be emulating SCSI for interfacing with the CD-ROM. (kernel 2.2, 2.4) If the CD was device /dev/hdb (example) it will now be the first CD-ROM SCSI device /dev/scd0. The emulation will now let your IDE CD-ROM act like a SCSI device. The old /dev/cdrom soft link should now be re-linked to the new device.
rm /dev/cdrom
ln -s /dev/scd0 /dev/cdrom
If using the lilo boot loader add the following line: (for CD device /dev/hdb)
append=" hdb=ide-scsi"
The module may be loaded manually with the command: insmod ide-scsi
You know you are successful when cdrecord -scanbus recognizes your CD-ROM drive.
- cdda2wav - a sampling utility that dumps CD audio data into wav sound files
- hpcdtoppm - convert a Photo-CD file into a portable pixmapmcd (RPM: netpbm-progs)
- ascd - An AfterStep and WindowMaker CD player
- xcdroast - CD-Writer Software
- FreeDB.org - The free alternative to CDDB
- CDDB: The motherload of CD databases
- xmcd: Motif based CD player with CDDB access.
Download/install: mkdir XMCD; cd XMCD; -download then-> tar xzf xmcdbin.tar.gz; su; chmod +x install.sh; ./install.sh
Config file: $HOME/.xmcdcfg/XMcd and /usr/X11R6/lib/X11/xmcd/app-defaults/XMcd
cron script to update local db: /usr/lib/X11/xmcd/scripts/genidx (Copy to /etc/cron.daily/)
Run: /usr/X11R6/bin/xmcd - MusicBrainz.org - CdIndex 2nd generation.
- CdChanger Jukebox application description - [Download]
- DiskMakers.com - Equipment for mass duplication, supplies.
- O'Reily: Creating Audio CD content
List of CDDB servers:
| freedb.freedb.org | cddbp 8880 | Requires no fees or registration |
| us.cddb.com | cddbp 8880 | Random US site |
| sc.ca.us.cddb.com | cddbp 8880 | Santa Clara, CA US |
| sc2.ca.us.cddb.com | cddbp 8880 | Santa Clara, CA US |
| sj.ca.us.cddb.com | cddbp 8880 | San Jose, CA US |
| sj2.ca.us.cddb.com | cddbp 8880 | San Jose, CA US |
Software to generate CD covers:
- CdLabelgen: home page - Generated postscript files. Integrates with gcombust CD burner software.
CD standards:
- Digital Audio CD-DA (Compact Disk Digital Audio) - "Red Book":
- Philips "redbook" standard - specifies the CD. stylus parameters, deviations and error rate, modulation system, error correction, sub-code channels, ...
- CD-R, CD-RW, Magneto-optical CD-MO and Write Once CD-WO - "Orange Book":
- ISO 9660 CD-ROM "High Sierra" - "Yellow Book":
- "Rock Ridge" CD-ROM Unix":
- Video CD vCD - "White Book":
DVDs allow for greater storage capacity. They are also different from CDs in that they must first be formatted. The growisofs command will perform this task automatically if it detects that the DVD is unformatted. The DVDs in these examples are burned DAO (Disk At Once).
Examples:
- Copy a simple video DVD with Linux:
- Rip: Create the ISO image with mkisofs as detailed above.
Copy a DVD and create ISO image file: (Paths reflect Fedora Core 3 / Linux kernel 2.6 mount point: /media/cdrecorder)
Examples:- mkisofs -pad -J -R -oCourtneyDVD.iso -graft-points "/AUDIO_TS=/media/cdrecorder/AUDIO_TS" "/VIDEO_TS=/media/cdrecorder/VIDEO_TS"
- mkisofs -dvd-video -oCourtneyDVD.iso -graft-points "/AUDIO_TS=/media/cdrecorder/AUDIO_TS" "/VIDEO_TS=/media/cdrecorder/VIDEO_TS"
(Use option -dvd-video to generate a DVD-Video compliant UDF file system. This will sort files appropriately and add padding. File video names must be in upper case.)
- Burn: Burn DVD with Linux and the growisofs command.
Since growisofs is also a front-end to mkisofs, one can append mkisofs commands:
Examples:- growisofs -dvd-compat -Z /dev/dvd=CourtneyDVD.iso -speed=2
Note: /dev/dvd and /dev/dvdwriter are soft links to /dev/hdc - Example of burning DVD using "dvdrecord":
- Linux 2.6 kernel: dvdrecord speed=1 -dao dev=ATA:1,0,0 CourtneyDVD.iso
- Linux 2.4 kernel: dvdrecord speed=1 -dao dev=1,0,0 CourtneyDVD.iso
- growisofs -dvd-compat -Z /dev/dvd=CourtneyDVD.iso -speed=2
- Rip: Create the ISO image with mkisofs as detailed above.
- Blanking a rewritable DVD: growisofs -Z /dev/dvd=/dev/zero
Not required before burning but erases sensitive data. - Burning a data DVD: growisofs -dvd-compat -speed=2 -Z /dev/dvd -R -J -pad /dir-path/file1 /dir-path/file2
- Burn data file to DVD: growisofs -Z /dev/dvd -R -J /dir/file-name
- Burning a data backup DVD using more mkisofs commands: (works on DVD+R and double layer DVD+R DL - Fedora Core 3)
- Example 1: growisofs -speed=8 -Z /dev/dvd -R -J -allow-multidot -allow-leading-dots -l -pad -graft-points "/home/user1=/home/user1"
(may not be DOS compatable because of long file name support, possible leading dot or multidot file names, but do you really care?) - Example 2: growisofs -dvd-compat speed=2 -Z /dev/dvd -R -J -pad -graft-points "/DirectoryNameA=/home/user1/DirectoryNameA" "/SubDirectoryNameC=/home/user1/DirectoryNameB/SubDirectoryNameC"
(write a DVD which MS/Windows can read - but not MS/DOS due to the "-l" option and long file names)
- Example 1: growisofs -speed=8 -Z /dev/dvd -R -J -allow-multidot -allow-leading-dots -l -pad -graft-points "/home/user1=/home/user1"
Usage: growisofs [growisofs-options] /dev/dvd [mkisofs-options]
growisofs command line options:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| -version | List version of program growisofs. |
| -Z /dev/dvd | Burn initial session to specified path. Closes DVD and no additions can be made. You can specify -Z or -M but not both. |
| -M /dev/dvd | Merge a new session to an existing one at the specified path. Multi-session. You can specify -Z or -M but not both. |
| -dvd-compat | Write with DVD compatibility. Write once disks are closed at the end of the session. |
| -dry-run | Perform steps but do not burn DVD. Checks for overburn condition (too much data for DVD). 4.7 Gbyte (4.7 x 10003) DVDs actually hold 4.377 Gb (4.3 x 10243) as measured by the computer system. |
| -overburn | Don't use this. Turns off overburn condition checking. |
| -speed=1 | Specify recording velocity. Recommend 1 or 2. Not as reliable as CDs for high speed burning. |
Note that the -R (Rock Ridge) and -J (Joliet) are mkisofs commands as described above which are appended to growisofs.
Formatting is not required as it is performed by the growisofs command if required. A DVD can be re-formatted using the command dvd+rw-format or to "erase" data.
[Potential Pitfall]: The automounter will detect a formatted DVD and mount it. You can not burn a mounted DVD. To disable the automounter, make sure the mount option "noauto" is used in the file /etc/fstab for the mount point /media/cdrecorder
/dev/hdc /media/cdrecorder auto pamconsole,exec,noauto, ... 0 0fstab man page
[Potential Pitfall]: Do NOT use the mkisofs option "-o" as this is unsupported with growisofs. There is no option to generate a file, you will be burning a DVD.
[Potential Pitfall]: If you hit the "memorylocked" resource limit and get the following error when issuing the growisofs (V6.0) command:
"unable to anonymously mmap 33554432: Resource temporarily unavailable"Issue the following bash shell command: ulimit -l unlimited
[Potential Pitfall]: If using the Linux 2.4 kernel (i.e. 2.4.18), you will have to apply kernel patches to get full DVD support. The 2.6 kernel (i.e. Fedora Core 3) has good built-in DVD support.
The following tools are included in the Fedora Core RPM package dvd+rw-tools:
- growisofs: Burn DVD. See tutorial above.
- dvd+rw-format: Format DVD. Also performed by growisofs if needed.
Format a DVD: dvd+rw-format -lead-out /dev/dvd
Usage: dvd+rw-format [-force[=full]] [-lead-out|-blank[=full]] [-ssa[=none|default|max]] /dev/dvd - dvd+rw-booktype: Utility for manipulating Book Type Field of Physical Format Descriptor located in lead-in of DVD+RW media.
Usage: dvd+rw-booktype [-dvd-rom-spec|-dvd+rw-spec|-dvd+r-spec|-inq] [-media|-unit|-unit+rw|-unit+r] /dev/dvd - dvd+rw-mediainfo: Information about mounted DVD media. Note: This never worked for me.
Usage: dvd+rw-mediainfo /dev/dvd - dvd-ram-control
Usage: dvd-ram-control [-arre] [-awre] [-rdonly|-rdwr] /dev/dvd
DVD Tools:
- Home page: dvd+rw-tools - [Download]
- growisofs.c - Source code.
- Burn a DVD with X-CD-Roast
- K3B CD/DVD Burner
DVD HowTos:
- Create video DVD from an AVI:
- MJPEG tools
[Download]
(Linux/Intel only due to use of Intels MMX instructions)
- MJPEG tools
[Download]
- Encoding with MPlayer: MEncoder
DVD Standards:
- ECMA-267: DVD Read Only disk
- ECMA-272: DVD Rewritable disk
- ECMA-274: Data interchange using +RW format
This command allows one to open and close the CD tray as well as control a multi-disk changer. Note that the first disk in a changer is referred to as disk "0", the second as disk "1", etc...
Samples:
- Open tray (eject): eject /dev/cdrom
(Fedora core 3 (kernel 2.6): eject /media/cdrecorder) - Open tray (eject) default CD device: eject
- Close tray: eject -t /dev/cdrom
- Rotate changer to second CD: eject -c 1 /dev/cdrom
There is rumor of a device driver for /dev/changer but I have no info on this.