Cross platform (Linux, MS/Windows, IRIX, Solaris (Gnome will be standard on Solaris 10))
- GTK.org: GTK+ (Cross platform)
- YoLinux tutorial: GTK+ Tips and Tricks - Building a GUI using GTK+
- Glade Home Page - GTK+ GUI builder.
- QT - Used to develop KDE (MS/Windows, Mac, Linux)
- wxWindows.org - Supports all platforms and many IDE's
- Fox Toolkit - Linux, Windows, most UNIX
- GLUT: Toolkit and GUI written in OpenGL. Cross platform MS/Win32 and X11
- Mozilla XPT - Can also use XML to define GUI layout
- OpenOffice.org: GSL
- Borland.com: CLX
- Winehq.com - Winelib - Libraries to support Windows API (Linux and BSD only. Not truly cross platform but a good porting tool)
- GNUstep: Gorm (Objective C)
- SL.com - Sherrill - Lubinski SL-GMS
Dynamic graphic GUI components and controls for real time interfaces and displays. Common ".m1" file graphic framework for C++ and Java. Graphic sources include Visio, bitmaps and DXF. Supports pan, zoom, drill-down and hyperlink capability. Supports input as well as displays. - Kinesix.com: Sammi - Similar to SL-GMS but not as good.
- Genlogic.com: GLG - Dynamic, data driven visual components.
- INT.com
- ILog.com: Views - Diagramming and data graphing capabilities.
- GNU C++ CGI
Programming web server CGI programs with C++ and the GNU CgiCC library - YoLinux Tutorial - CGILIB - Red Hat
- CppUnit: C++ Unit test framework. YoLinux CppUnit tutorial
- Google C++ Unit Test: Unit test framework used to mimic JUnit XML output. - YoLinux GoogleTest tutorial
- CxxTest - C++ test framework
- Unit++ - testing library and framework
The following IDEs will provide an integrated edit, build and debugging environment for C++ on Linux.
- # Eclipse/CDT
- # NetBeans (Sun)
- # KDevelop (KDE/Qt)
- # Anjuta (Gnome/GTK)
- # Code Dragon (for wxWindows development)
- # Code Warrior (by Freescale)
- # IDE Links
(IDEs are cross platform and are available on MS/Windows and other UNIX environments)
Written in Java, this IDE was originally developed for programming JAVA. Since its' inception, it was designed with a plug-in architecture to support other languages and programming needs. For C++ development, one must download the Eclipse CDT version for C++ which is platform dependent and processor word size dependent (32 bit/64 bit) and not the same download as the regular Java Eclipse IDE.
Eclipse Home Page
Download http://eclipse.org/downloads/ - i.e. eclipse-cpp-XXX-linux-gtk-x86_64.tar.gz
Eclipse also requires the Java installation. See YoLinux Java download/installation
Install Eclipse:
- for all on system:
- mv eclipse-cpp-XXX-linux-gtk-x86_64.tar.gz /opt
- tar xzf eclipse-cpp-XXX-linux-gtk-x86_64.tar.gz
OR - for yourself only:
- Download to your home directory.
- tar xzf eclipse-cpp-XXX-linux-gtk-x86_64.tar.gz
- Run Eclipse:
- /opt/eclipse/eclipse
- Icon for desktop launcher: /opt/eclipse/icon.xpm
- for all on system:
You may also want to include the following Eclipse plug-ins:
- Subclipse: Subversion plug-in for Eclipse
Installation:- Download site.0.9.36.zip to Eclipse directory: /opt/eclipse
- Unzip file (May require installation of RPM package unzip): unzip site.0.9.36.zip
- Start Eclipse IDE: /opt/eclipse/eclipse &
- In Eclipse select: "Help" (from menu bar) +
"Software Updates" + "Find and Install" (wait a minute or so for it to
respond. No joke, on slow systems expect to wait over 3 min.) + "Search
for new features to install" + "Next" + "New local site".
Browse to: /opt/eclipse/update/ + select "OK" - Select the box next to "eclipse/update" + "Next" + select the "I accept the terms ..." + "Next" + Features to install: select "Subclipse 0.9.36" + "Finish" + "Install All" + "Yes" to restart Eclipse.
- Select "Window" from the menu bar + "Open Perspective", select "Other...", select "SVN Repository Exploring", select "OK"
To add a new SVN repository: Right click in "SVN Repository" Exploring pane + right click "New", "Repository Location". In the "Add SVN Repository" window enter in the "Url:" space under "Location" the SVN location + select "Finish".
- Subversive: Another Subversion plug-in for Eclipse. Includes more details for advanced Subversion users. Displays lots of version info. Annoying if you want a clean simple interface.
- EHEP: Hex file viewer plug-in
- Eclipse VI plug-in - For those who love VI editing and cursor manipulation key bindings.
- List of Source Code Security Analyzers
[Potential Pitfall]:
If Eclipse is installed in /opt/eclipse/ for system wide use,
you may want to start Eclipse with the following command:
eclipse -data /home/user1/workspace
[Potential Pitfall]: When downloading Eclipse and Eclipse plug-ins, look at the README files (eclipse/readme/readme_eclipse.html) to see if you have a matching GTK+ release. If the version of Eclipse and plug-ins are too new for the version of GTK+ on your system then Eclipse may not display properly. For older versions of Linux, you may have to install older versions of Eclipse and older plug-ins. i.e. the latest version of Eclipse (3.1.1) on the older Red Hat Linux 8.0 will NOT operate properly. Eclipse 3.1.1 requires GTK 2.2.1 while Red Hat 8.0 uses GTK 2.0.
[Potential Pitfall]: Don't mix 32 bit Java with 64 bit (AMD64/EM64T) Eclipse. Choose all 32 or all 64 bit for Eclipse environment.
Error in ~/workspace/.metadata/.log
!SESSION 2005-10-31 00:19:28.817 -----------------------------------------------eclipse.buildId=M20050929-0840
java.version=1.4.2_09
java.vendor=Sun Microsystems Inc.
BootLoader constants: OS=linux, ARCH=x86_64, WS=gtk, NL=en_US
Command-line arguments: -os linux -ws gtk -arch x86_64
!ENTRY org.eclipse.osgi 2005-10-31 00:19:29.787
!MESSAGE Application error
!STACK 1
java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: /opt/eclipse/configuration/org.eclipse.osgi/bundles/24/1/.cp/libswt-pi-gtk-3139.so:
...xxxxxxxxxxx...: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
at java.lang.ClassLoader$NativeLibrary.load(Native Method)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadLibrary0(ClassLoader.java:1586)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadLibrary(ClassLoader.java:1495)
at java.lang.Runtime.loadLibrary0(Runtime.java:788)
at java.lang.System.loadLibrary(System.java:834)
at org.eclipse.swt.internal.Library.loadLibrary(Library.java:123)
at org.eclipse.swt.internal.gtk.OS.(OS.java:19)
at org.eclipse.swt.internal.Converter.wcsToMbcs(Converter.java:63)
at org.eclipse.swt.internal.Converter.wcsToMbcs(Converter.java:54)
at org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display.(Display.java:122)
at org.eclipse.ui.internal.Workbench.createDisplay(Workbench.java:381)
at org.eclipse.ui.PlatformUI.createDisplay(PlatformUI.java:155)
at org.eclipse.ui.internal.ide.IDEApplication.createDisplay(IDEApplication.java:128)
at org.eclipse.ui.internal.ide.IDEApplication.run(IDEApplication.java:79)
at org.eclipse.core.internal.runtime.PlatformActivator$1.run(PlatformActivator.java:226)
at org.eclipse.core.runtime.adaptor.EclipseStarter.run(EclipseStarter.java:376)
at org.eclipse.core.runtime.adaptor.EclipseStarter.run(EclipseStarter.java:163)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:39)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:25)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:324)
at org.eclipse.core.launcher.Main.invokeFramework(Main.java:334)
at org.eclipse.core.launcher.Main.basicRun(Main.java:278)
at org.eclipse.core.launcher.Main.run(Main.java:973)
at org.eclipse.core.launcher.Main.main(Main.java:948)
- Help/Welcome screen is default upon start-up and gives an introduction and tutorials on Eclipse . You can later return to this menu: "Help" + "Welcome".
- I could not find any way to enter gdb debugger commands. The only input accepted is through the GUI. While it offers similar capability to MS/VC++, hard core debugging is best left to ddd.
 This Sun IDE has refactoring support, profiler integration, fantastic cross referencing and navigation support (not limited to ctags) with code completion. It supports Qt development, Linux GNU, Cygwin and MinGW C/C++ compilers and GDB debuggers.
You can inspect the class inheritance hierarchy, a header's include hierarchy, the type hierarchy, and more.
It supports GNU Makefiles and C++ as well as language support for Java/Ant, Javascript, Python, Ruby, Groovy and PHP.
The only drawback I have experienced is running it remotely over the XMing MS/Windows X-server.
NetBeans is probably the most feature-rich C++ IDE available for Linux.
This Sun IDE has refactoring support, profiler integration, fantastic cross referencing and navigation support (not limited to ctags) with code completion. It supports Qt development, Linux GNU, Cygwin and MinGW C/C++ compilers and GDB debuggers.
You can inspect the class inheritance hierarchy, a header's include hierarchy, the type hierarchy, and more.
It supports GNU Makefiles and C++ as well as language support for Java/Ant, Javascript, Python, Ruby, Groovy and PHP.
The only drawback I have experienced is running it remotely over the XMing MS/Windows X-server.
NetBeans is probably the most feature-rich C++ IDE available for Linux.
Netbeans requires Java installations. See YoLinux Java download/installation
NetBeans for C++NetBeans C/C++ tutorial
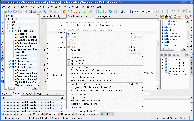 KDevelop has built-in Qt GUI development support (KDesigner), dOxygen auto-documentation support, makefile, ctags based navigation.
Subversion, CVS, Perforce and Clearcase CM client support is built-in.
KDevelop has built-in Qt GUI development support (KDesigner), dOxygen auto-documentation support, makefile, ctags based navigation.
Subversion, CVS, Perforce and Clearcase CM client support is built-in.
KDevelop provides cross platform support for MS Windows, Mac OsX, Linux, Solaris and FreeBSD. It also supports multiple languages such as C/C++, PHP ad Ruby as well as Automake, Make, qMake, CMake and Ant build systems. This IDE works and is simple to use.
Quick start (using existing C++/Makefile code):
- Start: kdevelop&
or start from Linux menu under "Programming". - Top tool bar: Project + Import existing project ...
- Directory: select for example ~/projectx/src
- Project name: ProjectX
- Project type: (default) Generic C++ Application (Custom Makefiles)
- OK
- Dialog box will ask if you want to populate with files recursively from the project directory: YES
- Select "File Tree" from left side tab to view files. Use right mouse button to invoke Subversion commands (i.e. update, commit, add, remove, ...)
- Generate CTAGS for file navigation: (navigate to function and variable declarations, etc)
- Select "CTAGS" tab on bottom
- Select "Regenerate" button
- Build (uses your make file):
Options:- Build project (will run makefile)
- Build target:
- cleanall
- clean
- all
- componenta
- componentb
- ...
Debugging: (GUI front-end to GDB)
- Top tool bar: Project + Project options...
- Icon on left: Select "Run Options":
- Directory: "Custom directory"
Select: ~~~/projectx/rundir/ - Program: ~~~/projectx/bin/Linux/program.exe
Set this to your executable you wish to run. - Program arguments: --arg1 abc --arg2 xyz (Select arguments which reflect your development)
- Environment Variables: Add to ~/.bashrc or add them here. See definitions above in this document.
- Ok
- Bring up program main: ~~/projectx/src/projectXmain.cpp
- Debug > Start
- Directory: "Custom directory"
- Icon on left: Select "Run Options":
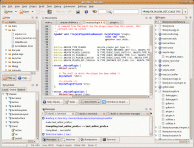 Anjuta
is a solid, simple, intuitive, bug free IDE for
C/C++ development on Linux. Search/Indexing, edit, compile and debug.
Anjuta supports Glade Gtk+ GUI builder, profiling (uses gprof) and memory leak detection (uses valgrind) and has an integrated help.
Anjuta
is a solid, simple, intuitive, bug free IDE for
C/C++ development on Linux. Search/Indexing, edit, compile and debug.
Anjuta supports Glade Gtk+ GUI builder, profiling (uses gprof) and memory leak detection (uses valgrind) and has an integrated help.
- YUM: yum install anjuta
- RPMs available from Dag Wieers: Anjuta.
- Ubuntu/Debian: apt-get install anjuta (requires: anjuta-common, libgtk2.0-dev libgtkmm2.0-dev libgnome2-dev libgnomemm2.0-dev devhelp-books glade-2 glade-gnome-2 cvs automake autogen indent ctags devhelp gnome-devel libtool)
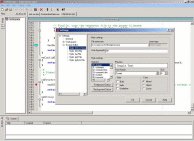 Code Dragon is an IDE which specifically supports the wxWindows cross platform GUI libraries which mimic Microsoft's GUI look and feel. The IDE itself was developed using wxWindows widget libraries.
Current support and development for this IDE seems to have been dropped although wxWindows development seems to be continuing.
Code Dragon is an IDE which specifically supports the wxWindows cross platform GUI libraries which mimic Microsoft's GUI look and feel. The IDE itself was developed using wxWindows widget libraries.
Current support and development for this IDE seems to have been dropped although wxWindows development seems to be continuing.
wxWidgets are cross platform and support Win32, Mac OS X, GTK+, X11, Motif, WinCE, and more.
Also see:
- wxGTK wxWindows rpms
Code Warrior (by Freescale - was Metrowerks) cross platform, also supports allot of embedded platforms, licensed commercial supported product. The CodeWarrior Development Studio contains all the tools needed to complete a major embedded development project (supports Freescale's IC and microcontroller products).
Also see:
- Getting Started with CodeWarrior IDE by Freescale video tutorial
Other C++ IDEs:
- OpenAmulet - DARPA funded, developed by the School of Computer Science at Carnegie Mellon University 1994-1997. No longer under development but source is still available.
- ICS BX Pro - Motif or Qt GUI builder, C/C++ IDE (commercial product)
- FLTK: Fast Light Toolkit - Cross platform C++ IDE. Supports GUI design and widgets from NEdit and its' own FLUID libraries.
- Scintilla
- Source Navigator - Based on Red Hat's original "source navigator" project. [screenshots]
- Slickedit - commercially developed and supported cross platform IDE for C/C++, Perl, Python and PHP. Has various modes including one which allows Slickedit to resemble Microsoft's Visual C++. Supports recordable macros, code navigation, code refactoring, auto-complete, diffs, etc.
- VDKBuilder - IDE specifically designed to support GUI construction using the VDK C++ GTK+ wrapper library. Uses SCONS and not Make for builds.
[Sourceforge project page] - WideStudio/MWT - Supports C/C++, Ruby, Perl, Python, Java. Cross platform: Win32, Solaris, MacOS, Linux, FreeBSD. Includes GUI builder/GUI code generator, OpenGL, ODBC, various language encodings.
- Xwpe-Alpha - Text console based IDE to mimic the old Borland MS-DOS C IDE. [screenshots]
- Use a combination of single purpose text console or GUI tools to edit (vi/vim/gvim, nedit, emacs/xemacs, gedit), navigate (ctags, cscope) and debug (GDB, ddd).
The following tools will provide the infrastructure for a C++ on Linux development environment:
- SCM (Software Configuration Management):
- Subversion CM server and Trac bug tracking server - version control - Subversion is a CVS follow-on with new features. Operates much like old CVS.
- IBM Rational Clearcase:
- YoLinux CM Tools links
- Bug / issue tracking:
- Trac bug tracking server - Installation, configuration and integration with Subversion.
- See YoLinux bug tracking systems links
- Build systems:
- GNU gmake/make: GNU make is a build system based on the original UNIX "make" build system but with more features. Install RPM package: make
GNU make manual - scons: Newer python based, cross platform build system. Great for cross platform development (i.e. MS/Windows and Linux/Unix)
- GNU gmake/make: GNU make is a build system based on the original UNIX "make" build system but with more features. Install RPM package: make
- Automated Nightly/Continuous Build and reporting systems:
- YoLinux Tutorial - Cabie Installation/Configuration: Multi-platform build system for Subversion, CVS or Perforce
- YoLinux.com: List of continuous and nightly build / test systems
- File Compare Tools:
- kdiff3:
Graphical directory and file diff, merge and edit. KDE3/Qt based.
Supports drag and drop. Comes with S.u.S.E. distro. (Cross platform)
MS/Windows download available.
- Difference: kdiff file1 file2
- Difference: kdiff file1 file2 file3
- Difference of two files: kdiff directory1/file directory2
- Difference: kdiff directory1 directory2
- Merge: kdiff directory1 directory2 -o dest-directory
- Merge: kdiff file1 file2 -m
- Merge: kdiff file1 file2 -o output-file
- Kompare: Ships with KDE SDK. [manual] default for RHEL 5/6
- Meld: Compare, edit and merge.
- tkdiff: [download]
- gvim and gvimdiff
- dirdiff: Directory difference viewer.
- kdiff3:
Graphical directory and file diff, merge and edit. KDE3/Qt based.
Supports drag and drop. Comes with S.u.S.E. distro. (Cross platform)
MS/Windows download available.
- Compiler: Install RPM packages for GNU compiler gcc, gcc-c++, binutils (linker), glibc, glibc-devel, gdb
Note:
- Also see Unit test frameworks
- Also see Javadoc like tagged comments the auto document generation facility: dOxygen - YoLinux Tutorial
- The above environment is cross platform and can be used on MS/Windows as well.
- Eclipse (and plug-ins) can be substituted by vi or emacs, ddd or gdb and raw svn commands.
If not pre-configured for software development, the following packages will have to be installed (at a minimum):
- Ubuntu: sudo apt-get install gcc g++ make autoconf automake gawk
- Red Hat: yum install gcc gcc-c++ make autoconf automake gawk binutils
The gcc/g++ compiler is compiled with a number of defined preprocessor variables. The list of defined variables compiled into gcc/g++ can be viewed by issuing the command: g++ -dumpspecs
The defined preprocessor variables can then be used to handle platform dependencies.
| Platform | Platform Variable Name | Variable: unix | Variable: posix | Variable: _POSIX_SOURCE | Architecture variable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCC: RHEL/Fedora Linux | linux __gnu_linux__ |
unix __unix__ |
* | __i386__ __x86_64__ |
|
| Red Hat 8 Linux | linux __gnu_linux__ |
unix __unix__ |
* | * | |
| Suse 9.2 Linux | linux __gnu_linux__ |
unix __unix__ |
|||
| Sun Solaris/SPARC | sparc | __arch64 | |||
| SGI IRIX/MIPS | sgi | unix __unix__ |
_SGI_SOURCE | mips host_mips |
|
| Cygwin Win/Intel-32 | __CYGWIN32 WIN32 |
unix __unix__ |
* | _X86_ |
Example C/C++ source code 1:
#ifdef sparc
...
#endif
#ifdef linux
...
#endif
#ifdef __CYGWIN32
...
#endif
...
#if defined(linux) || defined(sparc)
...
#endif
...
Example C/C++ source code 2:
#ifdef sgi
return fn_sgi();
#elif defined(__CYGWIN32)
return fn_win();
#elif defined(linux)
return fn_linux();
#else
struct time ts;
return fn_time();
#endif
...
OR
#ifdef sgi
#include file_sgi.h
#elif defined(sparc)
#include file_sparc.h
#elif defined(linux)
#include file_linux.h
#else
#error Unknown OS type
#endif
...
Note use of the "#error" for error processing.
Also see YoLinux GNU Makefile cross platform tips
Tips:
- Use macro for GNU C/C++ specific syntax, include files or macros: #ifdef __GNUC__
- Macros are not always defined in the same header files or perhaps in any at all. Check if defined, if not, include the proper file:
#ifndef DBL_MAX #include <float.h> #endif - Include files for an api are sometimes found in different files.
- access()
- Linux: #include <unistd.h>
- Solaris: #include <sys/fcntl.h>
- chown()
- Linux: #include <unistd.h>
- Solaris: #include <sys/types.h>
- time()
- Linux: #include <time.h>
- Solaris: #include <sys/types.h>
- access()
- Command paths of rm, mv, cp, etc are different for Linux and Solaris:
#ifdef linux sprintf(cmd,"/bin/mv"); #else sprintf(cmd,"/usr/bin/mv"); #endif - Hardware differences will have to be accounted for. SPARC is big endian and Intel x86 is little endian. Binary files and messages will be affected.
See our Big and Little Endian Byte Order conversion tutorial - Compiler command line options are different between the GNU and Solaris compilers.
- Resources:
- IBM Solaris to Linux porting guide - signals, thread library, make, etc
- Oracle porting guide
- Libraries unique to Solaris can be found in the Open Indiana (was OpenSolaris) GIT repository.
C Library source code: - CDE - Common Desktop Environment: CDE Sourceforge page [Download source
- Sun Xview/OpenLook: This was open sourced and can be downloaded and compiled.
Linux Xview/OpenLook resources
- Link error solution:
If you get a similar error ClassName::ClassName[not-in-charge]
The solution is to change the order of the libraries.
i.e. If the following compile results in an error:
g++ source-file.cpp -lxxx -lyyy -lzzz -L../XXX -L../YYY -L../ZZZ
The solution is to change the order of the libraries:
g++ source-file.cpp -lyyy -lzzz -lxxx -L../XXX -L../YYY -L../ZZZ
The order of the library paths is irrelevant (-L). - C++ Link error: "undefined reference to `vtable for classname-goes-here`"
My fix was to define a destructor. The virtual base class and destructor required the derived class to define a destructor. - Architecture independent data types and pointers:
- Avoid 32/64 bit cross platform issues by using pointer type: intptr_t
Use include file stdint.h. MS/Windows uses INT_PTR. - Avoid integer word size issues by using defined types in stdint.h
- Libraries are typically found in /usr/lib and /lib. On systems which mix 32 and 64 bit libraries look for /usr/lib64 and /lib64.
- Avoid 32/64 bit cross platform issues by using pointer type: intptr_t
- Include file paths:
Use colon separated include paths.Language Environment Variable C C_INCLUDE_PATH C++ CPLUS_INCLUDE_PATH Objective C OBJC_INCLUDE_PATH
Example: export CPLUS_INCLUDE_PATH=/opt/include:/opt/boost/include
Name mangling is the C++ compiler technique used to allow function overloading. It allows a function of one name to be used with multiple argument signatures. This is a "behind the scene" compiler operation which does not concern most programmers unless they link with object code generated by other languages including C.
The C++ compiler assumes name mangled function names where the function name includes the argument list data types. For example, the following functions have the following real names in object code symbol table:
| C++ function prototype | Function name in object code (symbol table) |
|---|---|
| void funcA(int) | funcA__Fi |
| void funcA(int, char) | funcA__Fic |
| void funcA(void) | funcA__Fv |
To view the function names in the object code, use the tool nm.
To prevent name mangling of C function calls, encapsulate the function declaration with extern"C".
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern"C" {
#endif
.
.
place declarations here
.
.
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
This is required because most programming languages including "C" do not name mangle function names.
For more details on GNU compiler name mangling see Dan Kegel's Name Mangling notes.
For linking with FORTRAN, see the YoLinux.com tutorial mixing C/C++ and FORTRAN.
- XmlBeansxx - Apache group C++ code generator to parse XML files based on a given XSD. Uses Xerces-C.
YoLinux.com XmlBeansxx tutorial - Xerces-C - Apache group XML parsing and query libraries.
YoLinux.com Xerces-C tutorials:- Xerces-C V3.0.1 tutorial
- Xerces-C V2.7.0 tutorial (used with XmlBeansxx)
- Gnome XML2 parsing library tutorial - C api
- C++ References:
- GNU C++ Library User's Guide
- Sun's C++ 5.0 Compiler Programming Guide - Very good coverage of advanced features
- C++ Programming Language Tutorials
- Cplusplus.com
- Informit.com: C++ reference guide
- C++ Library References:
- STL - home (SGI)
- C++ Data Structures Source Code
- List of C++ Libraries
- C++ Standard Library - A Tutorial and Reference - Nicolai Josuttis
- C++ API's and Toolkits:
- C++ Motif toolkit
- Object Oriented Programming - C++ GUI and C++ frameworks
- Cross Platorm Support Libraries:
- ACE C++ Framework - Schmidt
- C++ Boost libraries
- Apache Portable Runtime (APR)
- Pthreads Win32: Posix threads for MS/Windows
- C++ Links and Info:
- C/C++ Users Journal - Magazine articles
- FreshSources.com
- C++ Pitfalls - by Cay S. Horstmann
- Programmersheaven.com: C++ Links
- US chapter of the Association of C/C++ Users
- The comp.lang.c++ FAQ
- Coding Standards
- C-C++ Beautifier HOW-TO
- CPP-Home.com
- CSourceSearch.net - C/C++ database of searchable source code

 Books:
Books:





